I have been doing a lot of research on robo advisors. As my life gets busier, I am really trying to make things easy on myself. That includes how I invest my income which is why I’m looking into robo advisors. During my research I ended up creating a robo advisor comparison chart that I wanted to share. Hopefully this chart will help you determine which robo advisor you should choose, based on your investment goals.

What Is a Robo Advisor?
Uber disrupted the taxi business and made finding a clean and friendly ride easy. Amazon sold books, and is now disrupting both book sellers and other retailers. In investing, robo advisors are turning the investing world upside down.
A robo advisor uses technology to manage your portfolio rather than financial advisors or stock brokers. Your goals and risk tolerance mathematically determine what your portfolio will look like. Algorithms then manage the portfolio on an ongoing basis.
Software dynamically monitors your portfolio and adjusts it as required. For example, as you get older, the algorithms may alter your asset allocation to include more fixed income to reduce your exposure to equities. Whereas in the “olden days” a human would make this decision for you, now the computers do it based on research and best practices.
Benefits of Robo Advisors
The main benefit of using a robo advisor is lower fees. As I have discussed here, fees have a huge impact on investment performance. Traditional financial advisors have always been expensive, and now that these advisors are no longer needed, the savings get passed on to you. The average robo advisor fee structure is 0.15% to 0.75% compared to at least 1.0% plus expenses for traditional advisors. That will always mean more money in your retirement account.
The other main benefit is that robo advisors are accessible. A lot of traditional advisors will not even look at you if you have less than $100,000 to invest. It is simply not worth their time to take on clients with less than that. On the other hand, robo advisor accounts can be set up with as little as $5.
Robo Advisor Drawbacks
You should be aware of a few of the drawbacks of using robo advisors. First, robo advisors rely on limited client information. Questionnaires are used to determine asset allocation and risk tolerance levels, which can change over time. A good financial advisor will watch for this and adapt the portfolio. A robo advisor has no way of finding out if changes need to be made unless the client updates their data in the system.
Another drawback is that there is no one to hold your hand. Pure robo advisors can be incredibly impersonal, no matter how intuitive or personal the company makes the web interface. Robo advisors are not set up to answer questions or explain your portfolio. You need to trust the system and move on.
Even with these drawbacks, robo advisors are great alternatives if you know what you are getting into.
That said, there are different types of robo advisors. For example, Personal Capital combines algorithmic investing with a personal advisor. You get the best of both worlds, with lower fees than a traditional service.
In the next section I will present my robo advisor comparison chart so you can see how each service compares.
The Robo Advisor Comparison Chart
Before you check out the comparison chart, I want to show you a study that was done comparing the returns of various rob advisor services. This is important because it shows how different approaches have fared.
The following image from Condor Capital Management shows the 1-year returns for various firms, with Schwab and Personal Capital rounding out the top two.
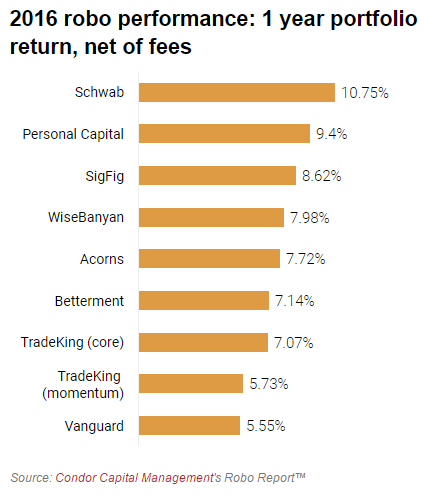
What is especially important about these results is that each firm has its own approach to asset allocation. Schwab had a higher than average exposure to emerging equities which paid off in 2016. Vanguard had a higher weighting to international (i.e. the U.K. and other larger European countries) which was hurt by the Brexit vote. Does this mean that Schwab is the better option? Not necessarily as you should not use one year performance metrics as a basis for your investment decisions. It simply highlights that each firm has a different approach.
With that in mind, here is the robo advisor comparison chart you can use to help guide your decision.
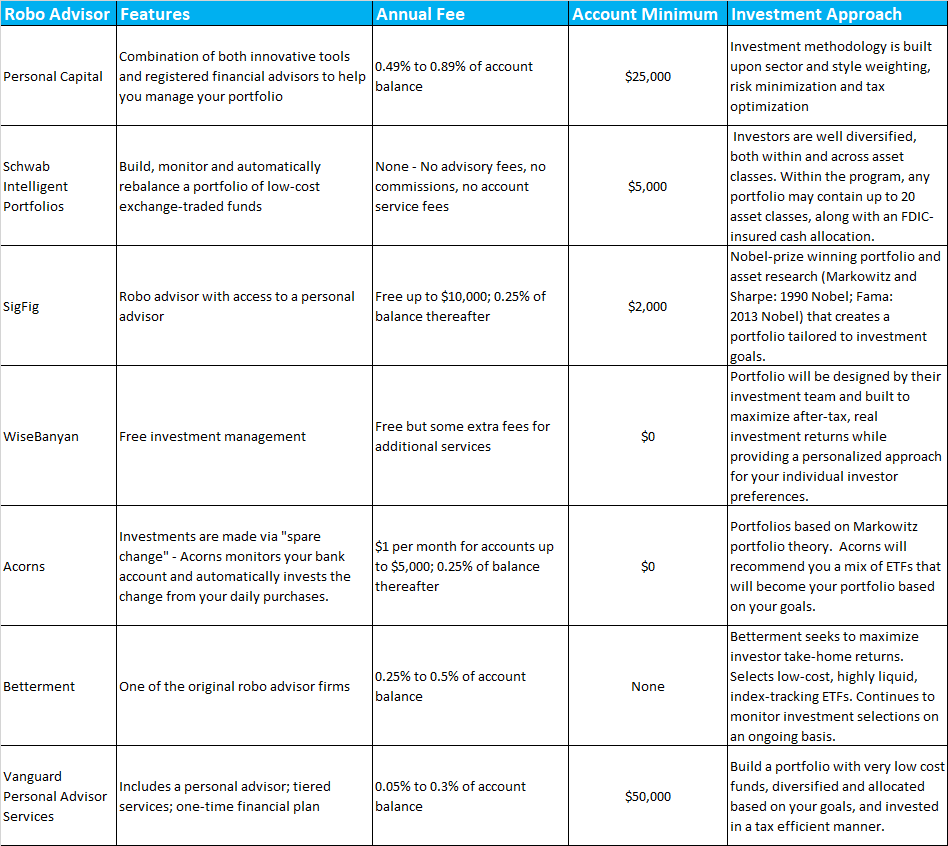
Which Robo Advisor Should You Use?
As you can see in the robo advisor comparison chart above, the primary differences between the firms is whether you get access to a personal advisor or not. Modern portfolio theory builds well-researched and solid portfolios. Portfolios are then created using a diversified set of assets that balance expected return with the risk profile of the investor. A solid portfolio, in specific allocations depending on your risk profile, is built with a combination of the following assets:
- U.S. Stocks – large and small
- International Stocks
- Emerging Market Stocks
- Real Estate
- Bonds – government and corporate
If they are all similar, which one should you use? My recommendation is Personal Capital. Even with their higher fees they have had solid performance and the personal advisors help you avoid the dumb emotional decisions that can wreck investment performance.
The primary reason for this recommendation is that they have a truly global approach to investing. As opposed to most U.S. investors who are way too “home country” biased, Personal Capital invests your funds globally in international stocks, emerging markets, as well as international fixed income. That alone is an important factor as there are huge growth prospects outside of the U.S. and I want to take advantage of that.
As always, make sure you do your own research on where to put your money. Make sure your goals and values align with the services you choose.
Have you made the jump to using a robo advisor? Which one did you choose and why? Let us all know in the comment section below.